Introduction to Measurement Tools
Measurement tools are essential instruments used to determine physical quantities. These tools help in obtaining precise and reliable measurements, which are useful across various industries and applications. From construction to healthcare, accurate measurements ensure effective planning and execution.
Measurement tools come in a variety of types. They range from simple devices like rulers to advanced instruments like laser measures. Each tool is specifically designed to measure a particular property, such as length, weight, temperature, or electrical parameters.
The selection of the right tool depends on the task’s requirements. Understanding measurement tools is crucial for achieving accuracy and efficiency. Whether for everyday use or specialized functions, they form the backbone of quality and precision in work.

Importance of Accurate Measurements
Accurate measurements are essential for ensuring efficiency and reliability in any task. Mistakes in measurements can lead to errors, wasted resources, and safety risks.
Why Accuracy Matters
- Enhances Efficiency: Proper measurements simplify processes and optimize resource usage.
- Ensures Safety: Precision reduces risks in industries like construction and healthcare.
- Improves Quality: Accurate data helps deliver better products and services.
- Saves Costs: Preventing errors means avoiding costly corrections later.
Fields Where Accuracy is Critical
- Construction: Exact dimensions prevent structural failures.
- Healthcare: Precise readings ensure patient safety.
- Manufacturing: Correct measurements ensure consistency and functionality.
- Research: Accurate data improves scientific outcomes.
Investing time in precise measurements is crucial for achieving success in any industry. Reliable measurement tools are the cornerstone of accuracy.
Common Categories of Measurement Tool
Measurement tools can be grouped into several common categories. Each category serves specific purposes and applications. Understanding these categories simplifies the process of choosing the right tool for a task.
1. Mechanical Measurement Tools
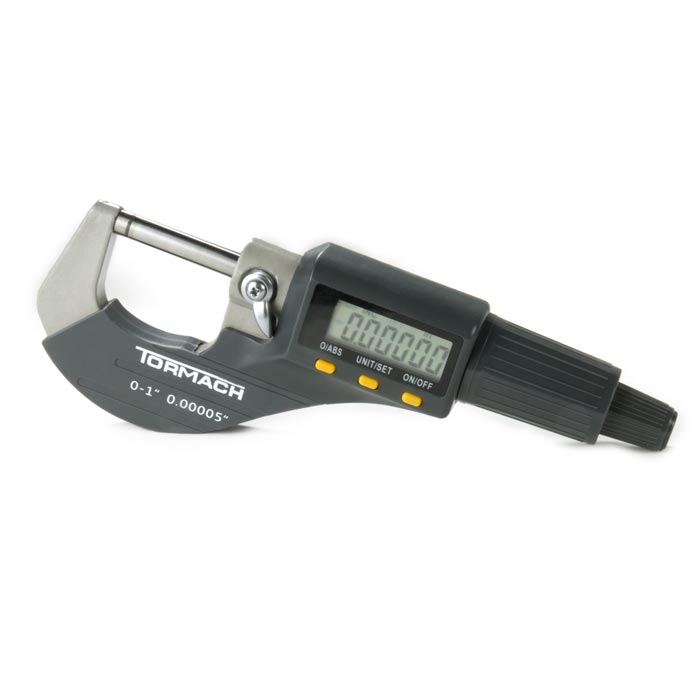
Mechanical tools measure physical properties like length, diameter, and thickness. Examples include rulers, calipers, and micrometers. They are highly valued for their precision.
2. Electrical Measurement Tools
These tools measure electrical parameters, such as voltage, current, and resistance. Common examples are multimeters and oscilloscopes. They are essential in electronics and electrical engineering tasks.
3. Digital Measurement Tools
Digital tools produce accurate and easy-to-read results. Examples include laser measures and digital thermometers. They are widely used in modern industries for fast and reliable measurements.
4. Specialized Measurement Tools
Some tools are designed for specific industries, like torque wrenches for automotive tasks or barometers for atmospheric pressure. These tools meet unique measurement needs in specialized fields.
By classifying measurement tools, users can quickly identify which tool suits their requirements. This ensures effective and efficient measurement practices.
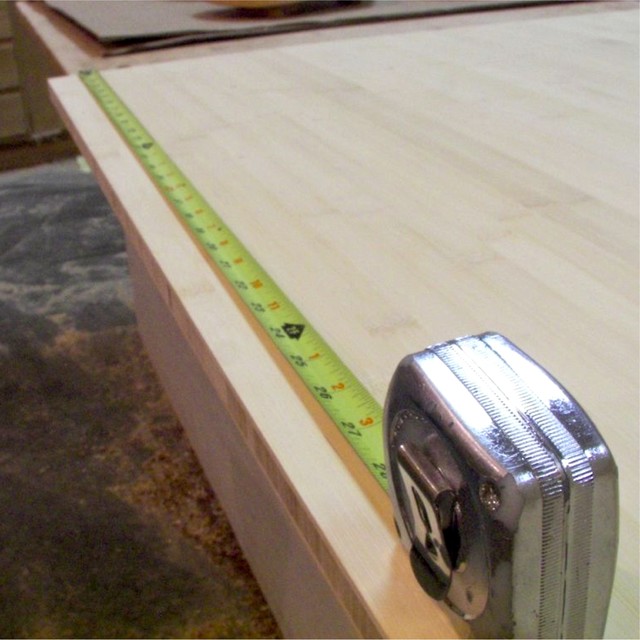

Mechanical Measurement Tool
Mechanical measurement tools are vital for determining physical dimensions and properties. These tools offer precision and simplicity, making them highly reliable for various tasks. Commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and quality control, they help achieve accuracy in measurements.
Rulers, Calipers, and Micrometers
- Rulers: Rulers are fundamental tools for measuring length or straight edges. They usually measure in inches, centimeters, or millimeters. They are simple, reliable, and perfect for basic tasks like drawing lines or measuring short distances.
- Calipers: Calipers measure dimensions inside or outside of an object. They excel at measuring diameters, depths, and widths. Vernier calipers, in particular, offer extremely fine measurements. Their versatility makes them popular in industries like engineering and machining.
- Micrometers: Micrometers measure very small distances with high accuracy. They are often used for objects too small for calipers. Mechanical micrometers are widely used for tasks requiring ultra-precise measurements, such as manufacturing parts or laboratory analysis.
These tools are essential for achieving precise and repeatable measurements. Their proper use ensures consistency and minimizes errors.
Electrical Measurement Tool
Electrical measurement tools are essential for monitoring and analyzing electrical parameters. They are commonly used in electronics and electrical engineering to ensure safety, efficiency, and proper functioning of systems. These tools measure key properties like voltage, current, and resistance, providing accurate data for diagnosis and troubleshooting.
Multimeters and Oscilloscopes
- Multimeters: Multimeters are versatile instruments that measure voltage, current, and resistance. They come in analog and digital versions, with digital ones being more widely used today. Multimeters are essential for electricians, offering quick and reliable readings. They help in diagnosing electrical problems, checking circuit continuity, and verifying equipment functionality.
- Oscilloscopes: Oscilloscopes measure the shape and characteristics of electrical waveforms. They display current and voltage signals graphically, allowing detailed analysis of circuits. Engineers rely on oscilloscopes to troubleshoot equipment, design electronics, and test signal integrity. Their ability to detect signal fluctuations makes them indispensable in many industries.
Digital Measurement Tool
Digital measurement tools are designed for fast and accurate assessments. They are widely used in industries due to their advanced features. These tools provide precise results with minimal effort, ensuring efficiency and reliability. Commonly, they feature easy-to-read displays and are ideal for modern-day applications.
Laser Measure and Digital Thermometers
Laser Measure:
- Laser measures use laser technology to determine distances and dimensions.
- They are popular for tasks requiring long-distance and high-precision measurements.
- Applications include construction, interior design, and real estate.
- Key advantages include speed, reliability, and usability in large spaces.
Digital Thermometers:
- Digital thermometers measure temperature quickly and with great accuracy.
- They are often used in healthcare, food safety, and environmental monitoring.
- These tools feature digital displays that make readings simple and clear.
- They help maintain critical conditions in temperature-sensitive processes or industries.
Digital tools are indispensable for professionals seeking accurate and consistent measurements daily.
Specialized Measurement Equipment
Specialized measurement equipment is designed to meet the unique demands of various industries. These tools cater to tasks that standard measurements cannot fulfill. They offer high precision and specialized functionality for specific applications. Industries often rely on these tools to achieve outstanding accuracy and efficiency.
Tools for Industry-Specific Applications
1. Torque Wrenches:
- Ensure proper tightening of bolts in automotive and mechanical work.
- Prevent over-tightening or loosening of critical components.
- Widely used in car manufacturing and repair.
2. Barometers:
- Measure atmospheric pressure for weather predictions and scientific research.
- Essential in meteorology and environmental sciences.
- Help track storm patterns and study climate conditions.
3. Flow Meters:
- Monitor liquid or gas flow rates in pipes and systems.
- Crucial for chemical processing, oil refining, and water management.
- Enhance system efficiency by regulating flow accurately.
4. Surface Roughness Testers:
- Analyze texture and finish of material surfaces.
- Key in industries focusing on quality control, like aerospace and machining.
- Ensure surfaces meet strict production standards.
5. pH Meters:
- Measure acidity or alkalinity in solutions.
- Common in food safety, pharmaceuticals, and environmental testing.
- Help maintain chemical balance in critical processes.
Specialized measurement tools empower industries to optimize performance and meet precise requirements. Their importance cannot be overstated in achieving high-quality results.
Tips for Selecting the Right Measurement Tool
Choosing the right measurement tool is crucial for achieving accurate and reliable results. It depends on understanding your task and matching the tool’s capabilities accordingly.
Factors to Consider
- Type of Measurement Needed: Identify the specific property to measure—length, weight, temperature, or voltage.
- Accuracy Requirements: Determine how precise the measurement needs to be for your application.
- Environment of Use: Consider if the tool will work in harsh, wet, or high-temperature conditions.
- Ease of Use: Select tools with user-friendly features and intuitive displays to simplify operations.
- Portability: If mobile use is required, opt for lightweight and compact measurement devices.
- Durability: Look for tools made from high-quality materials for long-term reliability.
Choosing by Category
- Mechanical Tools: Ideal for measuring physical dimensions like thickness or length in everyday tasks.
- Electrical Tools: Choose these for electronics-related work, such as checking voltage or resistance.
- Digital Tools: Great for fast and modern-day measurement solutions, like distance or temperature.
- Specialized Tools: Select these for industry-specific measurements, such as torque or fluid flow rates.
Practical Tips
- Always read user reviews before purchasing a measurement tool.
- Invest in tools from trusted brands that offer warranties and support.
- Check if the tool meets industry standards relevant to your work.
- Match the tool’s capabilities to the complexity of your task.
Taking these considerations into account ensures you choose a tool suited to your needs. Proper selection avoids errors and maximizes efficiency.

Maintenance and Calibration of Measurement Tool
Proper maintenance and calibration of measurement tools are essential for ensuring their accuracy and longevity. Regular upkeep not only prolongs the lifespan of these tools but also delivers reliable measurements consistently.
Importance of Maintenance
- Prevents Wear and Tear: Regular checks prevent excessive damage and extend the tool’s life.
- Ensures Accuracy: Properly maintained tools continue to deliver precise results over time.
- Reduces Costs: Avoid frequent replacements with proper care and handling.
- Improves Safety: Well-maintained tools minimize errors that can result in safety risks.
Tips for Maintaining Measurement Tools
- Clean After Use: Wipe tools to avoid dust, dirt, or residue buildup.
- Proper Storage: Store tools in a clean and dry space to prevent damage.
- Avoid Overloading: Use tools within their specified limits to prevent strain or malfunction.
- Inspect Regularly: Perform periodic visual checks for signs of damage or wear.
- Protect from Moisture: Avoid exposing tools to moisture, especially electrical ones, to prevent corrosion.
Importance of Calibration
Calibration ensures that measurement tools provide accurate readings. Over time, tools can drift from their original settings, affecting their precision.
Steps for Calibration
- Determine Frequency: Calibrate tools at regular intervals based on usage frequency and manufacturer recommendations.
- Use Certified Standards: Compare measurements with certified reference standards for accuracy.
- Log and Record: Keep records of calibration dates and results for traceability.
- Seek Professionals: For complex tools, rely on certified calibration services.
Tools That Require Frequent Calibration
- Digital Measurement Tools: Devices like laser measures and digital thermometers need periodic recalibration.
- Electrical Measurement Tools: Multimeters and oscilloscopes should be recalibrated for consistent performance.
- Specialized Tools: Instruments like torque wrenches and flow meters require regular calibration for industry compliance.
By incorporating regular maintenance and calibration practices, users can ensure their measurement tools remain accurate and dependable. Neglecting these steps may lead to errors, impacting work quality and safety.
The Impact of Technology on Measurement Tool
Advances in Digital Measurement Instruments
Technology has significantly transformed the landscape of measurement tools, particularly with the introduction of digital instruments. Digital measuring devices such as laser distance measurers and digital calipers offer improved accuracy and ease of use. With features like digital displays and memory functions, these tools simplify the measurement process and reduce human error. The seamless integration of technology allows professionals to perform tasks more efficiently, providing precise measurements at the push of a button. As industries evolve, investing in digital measurement tools can help keep pace with modern demands and enhance overall productivity.
Software Integration and Data Management
Modern measurement tools are increasingly being integrated with software solutions that enable data management and analysis. For instance, advanced laser distance measurers can connect to smartphones or tablets, allowing users to log measurements, create floor plans, and share data in real-time. This integration promotes collaboration among teams and improves project efficiency. In industries such as construction and engineering, data-driven decision-making is becoming commonplace. Utilizing measurement tools that offer software capabilities can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your operations, providing valuable insights that drive results.
The Importance of Training and Expertise
As measurement tools become more advanced, it is crucial for professionals to receive proper training on their use and maintenance. Understanding how to operate digital instruments effectively, as well as interpreting the data they provide, is essential for accuracy. Many manufacturers offer training resources and tutorials to help users maximize the capabilities of their tools. Investing time in ongoing education not only improves the skill set of individuals but also enhances overall workplace safety and productivity. As technology continues to develop, staying informed about the latest trends and tools will enable professionals to work more effectively in their respective fields.
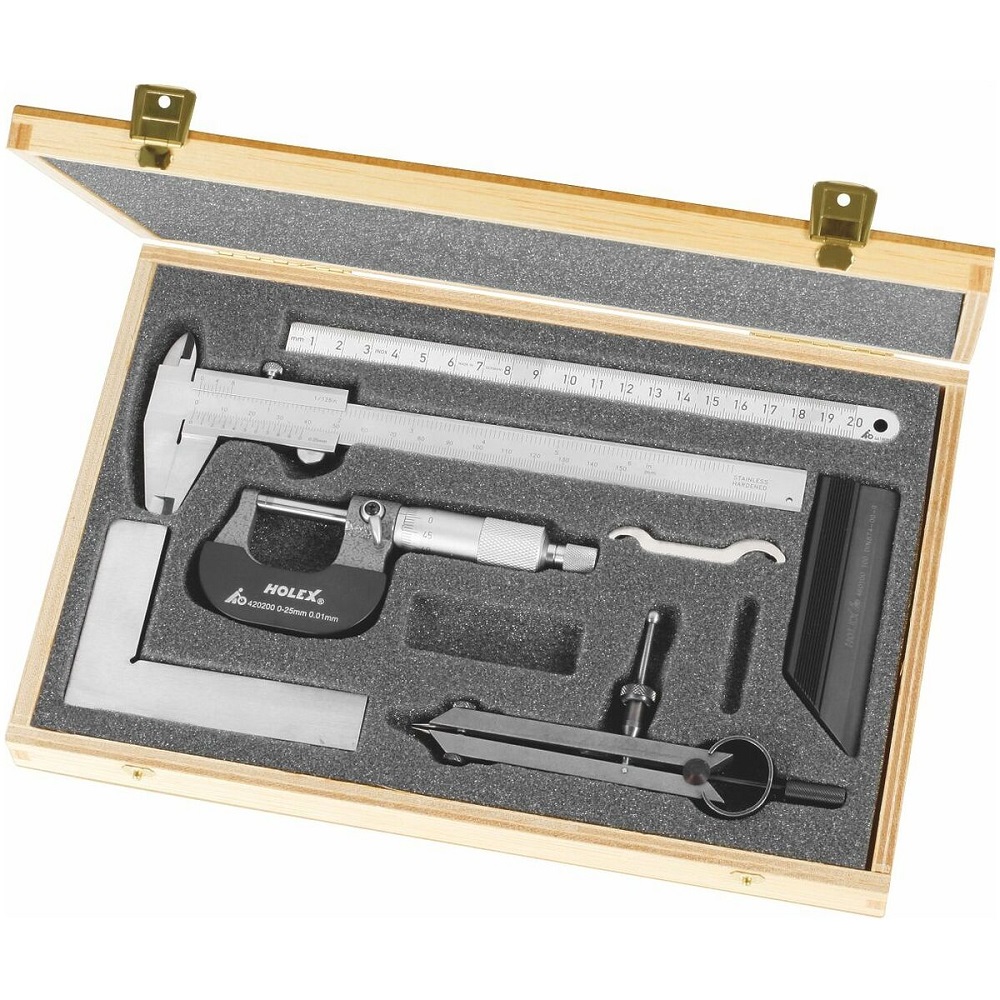

Conclusion: Achieving Precision with the Right Measurement Tools
Recognizing the Value of Accuracy
Ultimately, precise measurements are integral to success in many professional environments. The right measurement tools play a pivotal role in ensuring that projects are completed to specification, products meet quality standards, and decisions are based on accurate data. Professionals who prioritize the use of reliable measurement instruments will create a framework for achieving high-quality results. In a continually evolving work landscape, being equipped with the right tools and knowledge is more important than ever.
Encouraging a Culture of Quality
Encouraging a culture of quality and accuracy within an organization can have far-reaching benefits. When employees recognize the importance of precise measurements, they become more invested in their work. Providing access to high-quality measurement tools and training will foster an environment where employees feel empowered to take pride in their craftsmanship. This culture directly contributes to enhancing the overall reputation of a company, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Moving Forward with Confidence
As you navigate your professional journey, remember the significant role that measurement tools play in your success. By embracing technological advancements, investing in quality instruments, and committing to ongoing training, you will enhance your ability to deliver exceptional results. Move forward with confidence, knowing that accuracy, reliability, and the right tools set the stage for achieving your professional goals. In the world of precision, the commitment to effective measurement will not only benefit you but will also contribute to the excellence of your entire field.





