Introduction: The Art and Science of Locksmithing
Understanding locksmithing
Locksmithing is an age-old trade that combines skill, knowledge, and meticulous attention to detail. The primary role of a locksmith tools are to work with various locking mechanisms, either to help people gain access when they’ve locked themselves out or to create secure systems for homes, businesses, and vehicles. Whether dealing with traditional locks and keys or modern electronic access systems, locksmiths play a critical role in maintaining security and safety.
The Importance of Quality Tools
At the core of a locksmith’s ability to perform their duties efficiently lies their toolkit. Quality locksmith tools are crucial for effective locksmithing, allowing professionals to address various situations, such as lockouts, lock repairs, and installations. An effective toolkit not only increases a locksmith’s efficiency but also impacts the quality of work delivered to customers. In this article, we’ll explore the essential tools every locksmith should have in their toolkit, along with tips on how to use them effectively.
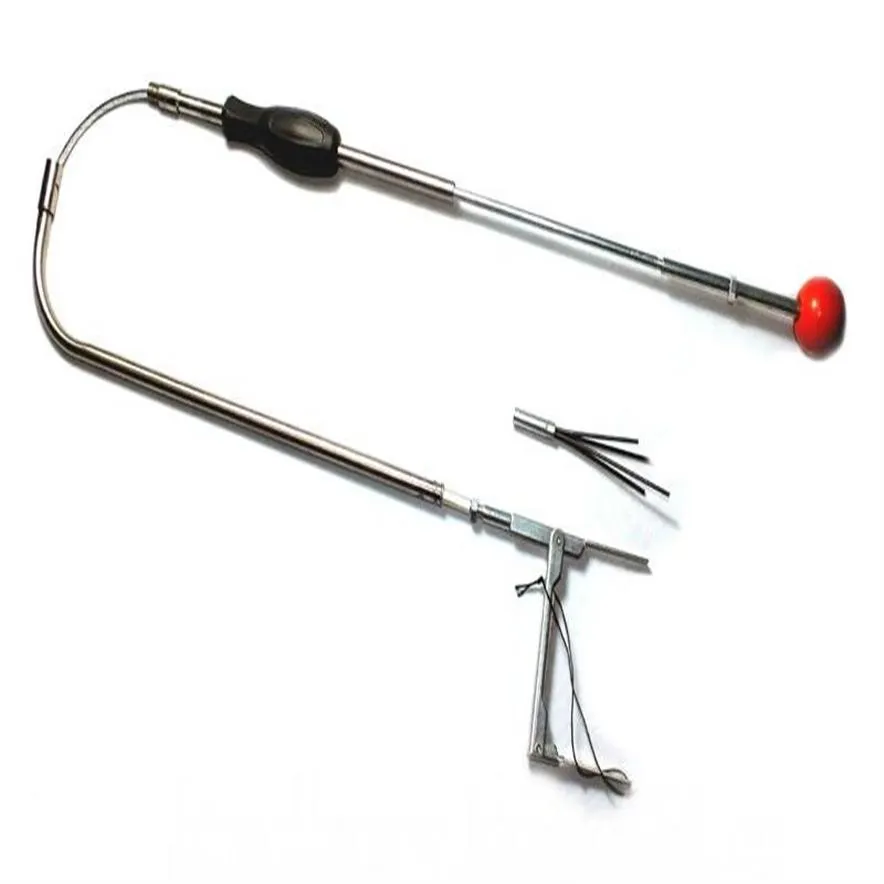

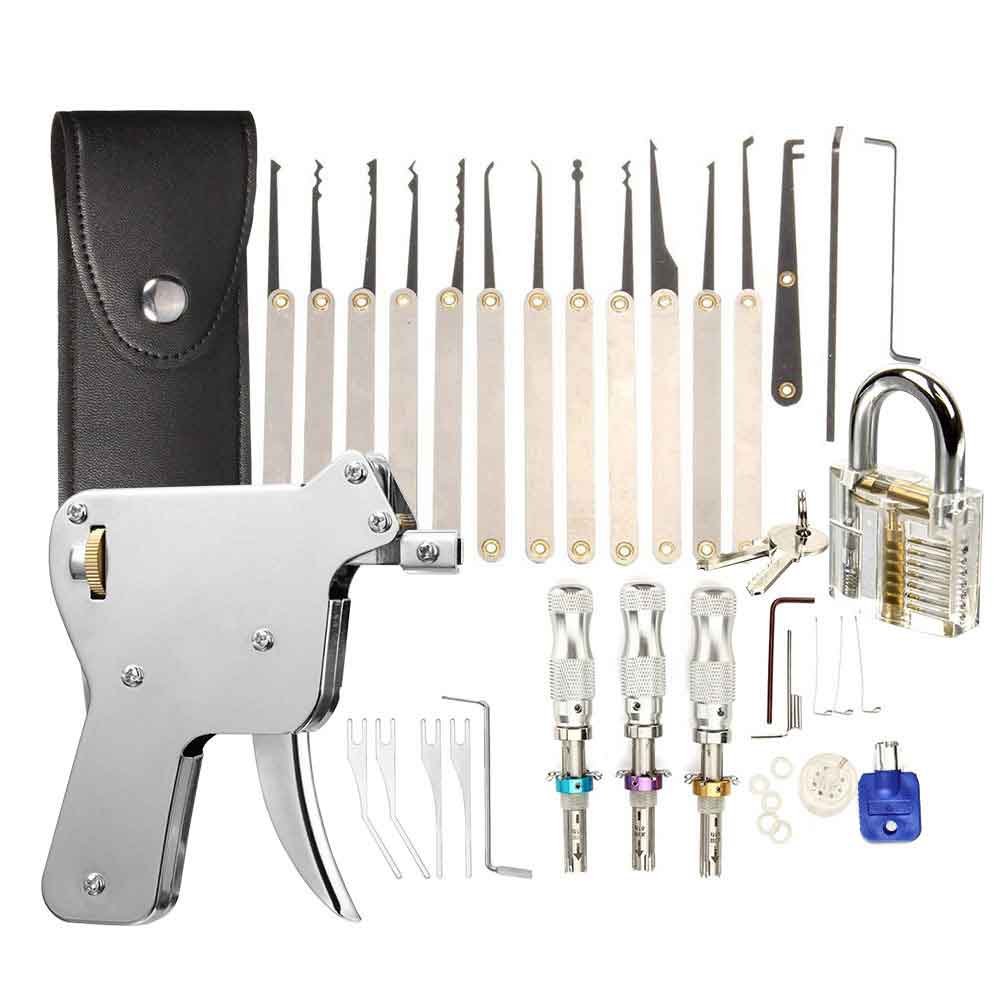
Essential Locksmith Tools
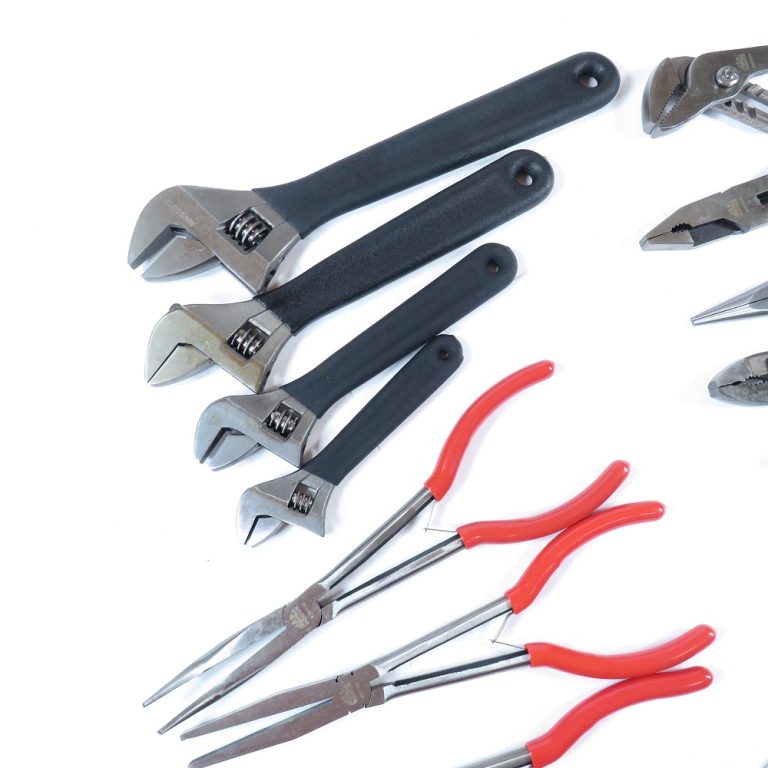
1. Basic Hand Tools
A Foundation of Skills
Before venturing into specialized equipment, locksmiths require a solid foundation built on basic hand locksmith tools. These are indispensable for both beginners and seasoned professionals alike.
- Screwdrivers: A variety of screwdrivers is necessary for different locks and door installations—flathead and Phillips screwdrivers are the most common. Precision screwdrivers can also be useful for dealing with smaller screws found in locks and electronic devices.
- Pliers: A pair of pliers, preferably needle-nose and regular pliers, is vital. Pliers are versatile tools used to manipulate, grip, and twist various lock components. They can also help in removing stubborn screws or pins.
- Hammers: A locksmith’s hammer is useful for tapping out stubborn locks and striking items that require force. By applying gentle pressure through hammering, a locksmith can make adjustments without damaging the lock.
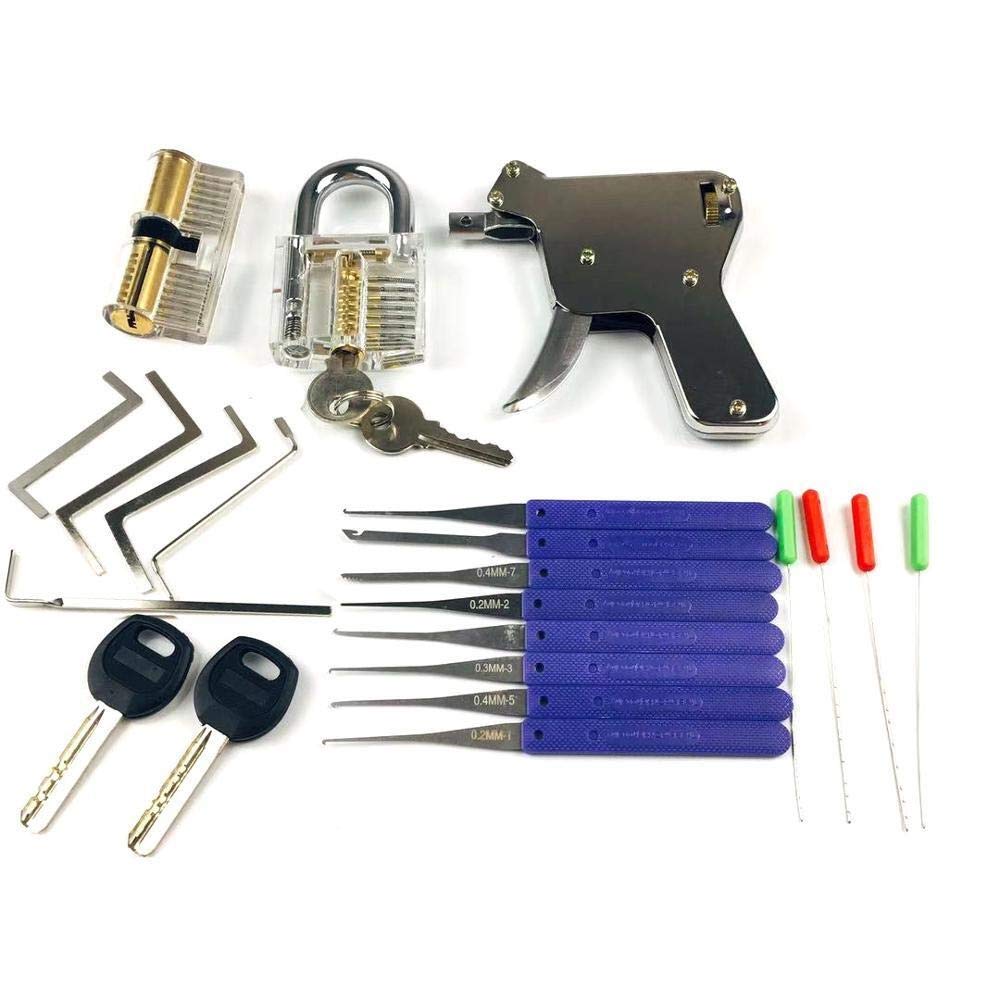
2. Lock Picks and Tension Wrenches
Unlocking Mysterious Mechanisms
Lock picking is an essential skill for locksmiths, and having the right tools makes this process much more efficient.
- Lock Pick Set: A comprehensive lock pick set includes a variety of picks and tension wrenches designed for different types of locks. Common picks include hook picks, rake picks, and diamond picks. Each pick type caters to specific lock mechanisms, making it easier to manipulate the pins inside locks.
- Tension Wrenches: Tension wrenches are necessary for maintaining pressure on the lock cylinder while inserting picks. They come in various shapes and sizes, and a locksmith should choose the one that fits comfortably in their hand while providing the necessary torque to turn the lock.
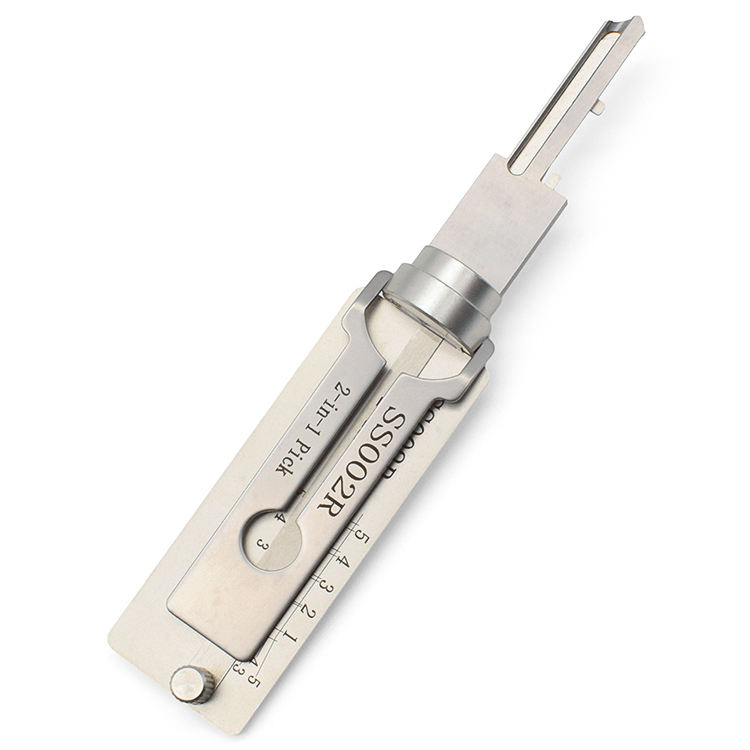

3. Key Cutting Tools
Creating New Access Points
Key cutting tools are among the most important tools in a locksmith’s kit, enabling them to provide new keys quickly and accurately.
- Manual Key Cutting Machine: A manual key cutting machine enables locksmiths to create duplicate keys. This machine uses a manual technique to trace the original key’s shape and cut a new one based on it.
- Electric Key Cutting Machine: An electric key cutting machine optimizes the key duplication process, allowing for faster and more precise cuts. Electric machines are especially handy when dealing with multiple key duplicates in a short timeframe.
4. Lock Installation Tools
Ensuring Security for Clients
When it comes to securing homes and businesses, accurate lock installation is critical. Locksmiths need specific tools to facilitate this process.
- Drills: A standard drill, along with a set of drill bits, enables locksmiths to create holes for installation. A rotary hammer drill can be especially useful in dealing with concrete or masonry.
- Chisels: Chisels are utilized for creating or modifying door frames and installing locks. Various sizes enable locksmiths to work with different thicknesses and designs.
- Measuring Tools: Accurate measurements are crucial for successfully installing locks. A tape measure, square, and level can help ensure that installations are precise and meet industry standards.
5. Automotive Locksmith Tools
Specialized Gear for Vehicles
With the rise of modern automotive technology, locksmiths have adapted their toolkits to address unique vehicle-related challenges.
- Slim Jim Tool: A slim jim is a flat strip of metal that locksmiths can use to unlock vehicle doors without a key. By sliding the tool between the window and weather stripping, it allows the locksmith to manipulate the locking mechanism.
- Car Opening Tools: These tools include various grabs, wedges, and inflatable bags that create space to access the lock mechanism without damaging the vehicle’s interior.
- Transponder Key Programmer: As modern vehicles increasingly utilize electronic ignition systems, locksmiths must invest in the technology to program transponder keys and remotes. This tool allows them to create and program new keys for vehicles equipped with electronic locks.
6. Security Tools
Maintaining Safety
Locksmiths also focus on enhancing security both for their clients and in their line of work.
- Security Cameras: Installing security cameras can help locksmiths protect their workplaces and secure their equipment. High-definition cameras can provide valuable footage in case of theft or vandalism.
- Alarm Systems: Integrating alarm systems into the locksmith’s toolkit helps them offer complete security solutions for clients. Being knowledgeable about alarm installation and shortcuts gives locksmiths an edge in providing comprehensive services.
Essential Skills for a Locksmith
1. Understanding Lock Mechanisms
The Importance of Knowledge
An in-depth understanding of various lock types and mechanisms is crucial for effective locksmithing. Familiarity with traditional pin tumbler locks, combination locks, and high-security options enables locksmiths to choose the correct tools and techniques for each job.
2. Skillful Manipulation
The Art of Lock Picking
Developing the skill to manipulate locks successfully is a cornerstone of locksmithing. Mastery of lock picking techniques and the ability to apply tension correctly can be valuable when unlocking a door without a key, gaining experience through practice on various lock types.
3. Customer Interaction
Building Trust and Client Relationships
Locksmithing often involves working with clients during stressful situations—such as being locked out of their homes or vehicles. Being courteous, professional, and communicative fosters client trust and confidence in their locksmith’s abilities.
Creating a solid reputation through excellent service and reliability can lead to repeat business and referrals.
Best Practices for Locksmiths
1. Continued Education and Training
Keeping Skills Updated
The locksmithing industry is continually evolving; hence constant education is crucial for staying current with the latest technologies and practices.
- Certifications: Pursuing relevant certifications can enhance a locksmith’s credibility. Organizations such as the Associated Locksmiths of America (ALOA) offer professional development programs, workshops, and courses to help locksmiths grow their skills.
- Staying Informed: Following industry news, technologies, and trends enhances a locksmith’s knowledge base. Engaging with professional organizations and participating in workshops can significantly contribute to skill improvement.
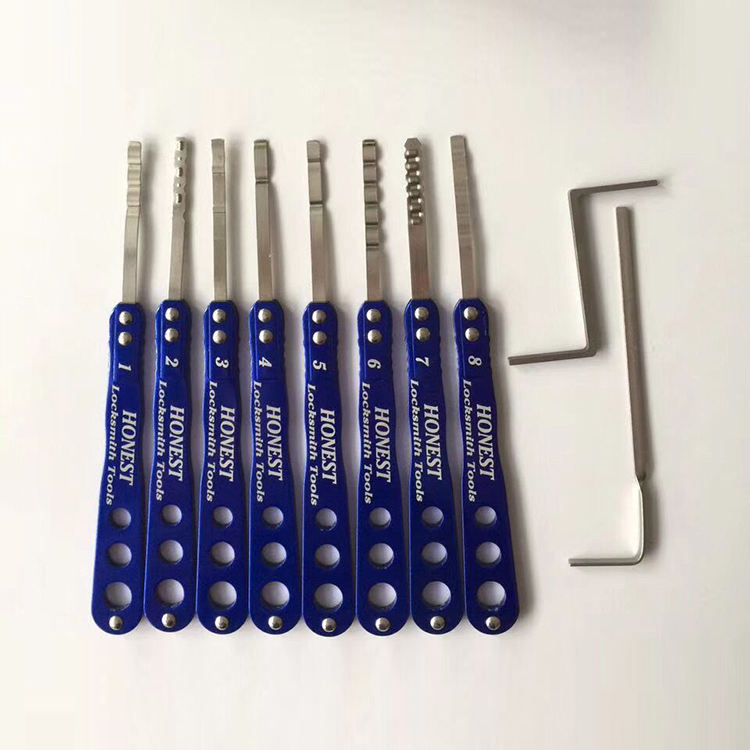

2. Proper Tool Maintenance
Caring for Your Toolkit
To ensure tools are functional and effective, proper maintenance is essential.
- Regular Cleaning: After each job, clean your tools to remove dirt, grime, and debris. This practice helps prevent rust and prolongs the life of your equipment.
- Routine Inspections: Regularly inspect your tools for signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Address any issues immediately to avoid complications or inefficiencies during future jobs.
3. Safety Practices
Prioritizing Personal Safety
While locksmithing is often safe, adhering to safety practices is essential to protect oneself while on the job.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wearing appropriate gear, including gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing, minimizes risk during installations and repairs, especially when using power tools.
- Safe Working Habits: Follow safe working procedures, especially when operating machinery or power tools. Familiarize yourself with safety protocols to prevent injury.
Conclusion: Mastering the Locksmith Profession
Embracing the Craft
Being a locksmith is both an art and a science, requiring a deep understanding of mechanics, security, and customer service. By equipping yourself with the essential locksmith tools and skills outlined in this article, you can elevate your locksmith proficiency and cater to the diverse needs of your clients.
Continuous Improvement
Owning quality tools is just as vital as honing your skills. Commit to continuous learning and best practices, and stay engaged with industry developments to remain relevant in this ever-evolving profession.

Delivering Excellence
Serving clients with professionalism and expertise fosters trust and loyalty, allowing you to build lasting relationships within your community. Approach each job with integrity, ensuring you provide high-quality service and secure solutions that put your clients first.
The Path Ahead
As you navigate your journey in locksmithing, remember that every interaction, every installation, and every challenge is an opportunity to learn and grow. With dedication to your craft, the right locksmith tools for home security, and a commitment to excellence, you can build a successful locksmithing career that leaves a lasting impression on everyone you serve.







